How AI search is changing the customer journey
Over the past two years, the rise of artificial intelligence has been as rapid as it has been profound. It’s not only transforming the way we work — it’s reshaping how we search for information, make decisions, and interact with brands. LLM-based tools like ChatGPT and Gemini are no longer a passing trend; they’ve become part of our daily routines and are redefining the customer journey at its core.
Today, users don’t just turn to these assistants for quick answers; they rely on them to discover products, compare options, and decide what to buy. And this shift in behavior signals the start of a new era for brands — one where visibility in traditional search engines is no longer enough.
In this article, we will take a deep look at how AI-driven search is rewriting every stage of the customer journey — from discovery to retention — what it means for attribution, why users now arrive at conversion points “pre-sold,” and what brands must do to stay visible and relevant as more decisions happen outside traditional search engines. Our goal is to provide a clear and practical framework that helps any organization understand this shift and prepare for it strategically.
Why AI search is rewriting the customer journey
To understand why AI search is fundamentally reshaping the customer journey, it’s essential to first look at how it works — especially compared to traditional search engines.
Since its launch in 1998, Google (along with other search engines like Bing) has relied on an index-based retrieval system: users type a query, the engine scans its index, and it returns a ranked list of webpages. For more than two decades, this model has shaped how people discover information, evaluate options, and ultimately choose what to buy. It also established the rules of SEO: brands compete for keywords, optimize pages, and earn links to climb higher in search results.
AI search breaks that model.
Instead of retrieving a list of links, LLM-based assistants interpret the query, reason about it, and generate an answer by synthesizing information from multiple sources they consider relevant. Relevance is no longer driven primarily by keyword rankings but by signals such as intent, context, entity relationships, freshness, user behavior, and overall source reliability.
The interaction feels more conversational, more direct, and requires fewer steps from the user. As a result, the customer journey becomes shorter, more guided, and often bypasses traditional touchpoints — including the brand’s website.
This is also where we see the shift from classic SEO (Search Engine Optimization), focused on ranking webpages for specific keywords, to GEO (Generative Engine Optimization), where the real challenge is to become the trusted source that generative engines learn from, reference, and build their answers on.
A practical example
If we search for the best barbershop in New York, we instantly see how differently each system operates.
1. Google Local Pack
Google first shows the local pack — a set of nearby businesses selected based on proximity, relevance, reviews, reputation, profile activity, NAP consistency, and user engagement.
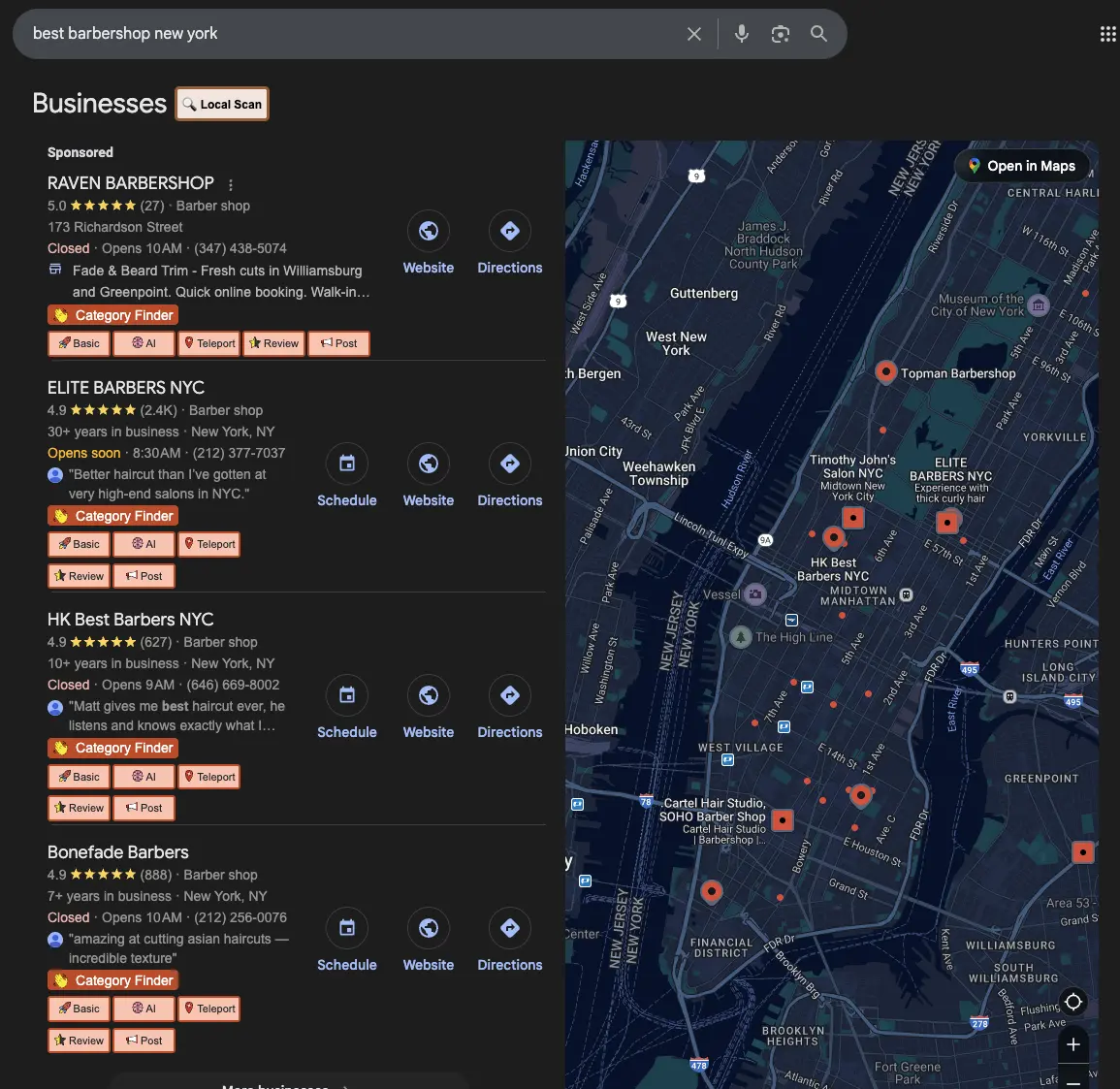
2. Organic search results
Below the local pack, we see the first organic rankings. These results differ because they are determined by traditional SEO factors such as content quality, backlinks, search intent alignment, and on-page optimization.
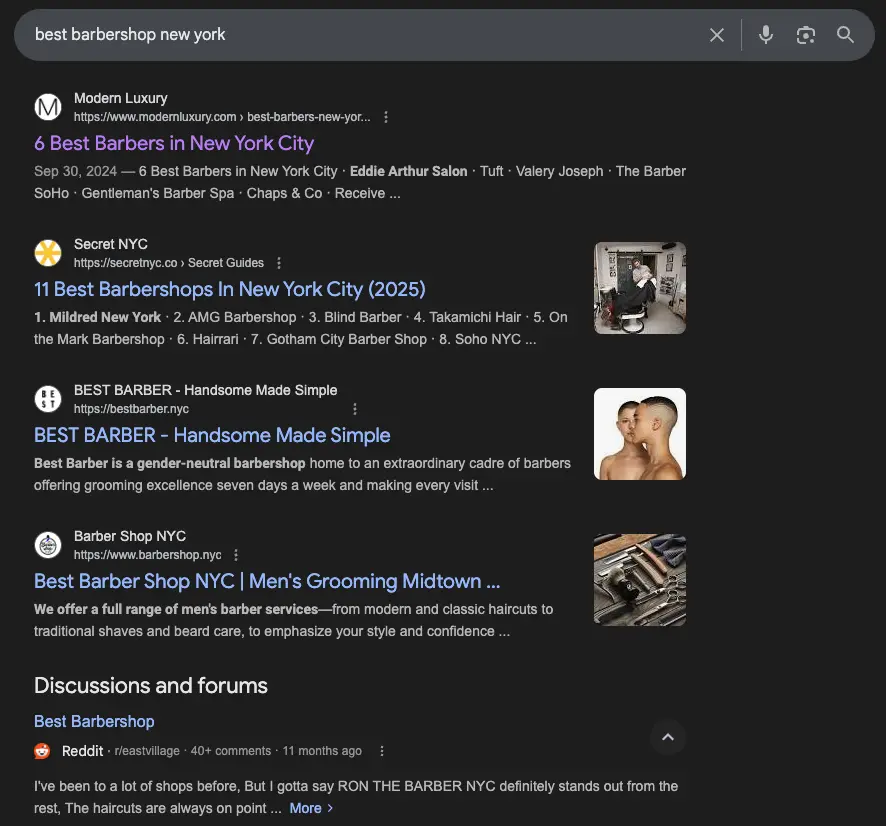
3. AI assistants (ChatGPT, Gemini)
If we ask ChatGPT the same question, it produces a different answer — one that does not directly match Google’s top results. That’s because AI assistants do not “pull” ranked links; they infer what business best matches the intent by evaluating broader contextual signals, reputation across the web, and how consistently that business appears as a trusted entity.

Why this shift matters
This evolution fundamentally reshapes how brands gain visibility and influence decisions:
Users now receive answers instead of options.
Product discovery increasingly happens inside AI assistants, not only on SERPs.
Brand visibility depends more on contextual authority than on traditional rankings.
Many buying decisions are made before the user ever reaches a website.
In this new environment, the entire funnel becomes a conversation, seamlessly blending discovery, consideration, and conversion. Visibility becomes pre-click: AI systems surface products and brands before the user lands anywhere, replacing keyword-driven ranking with AI-driven selection based on relevance, authority, and context.
Awareness – How AI search changes product discovery
AI search is reshaping the awareness stage more radically than any other phase of the customer journey. While traditional discovery, either paid or organic, unfolds in a linear sequence — search, scroll, compare, filter, refine — AI flips that model entirely.
Instead of requiring users to sift through pages of results, AI assistants pre-curate the options. They interpret the intent behind the query, filter out irrelevant noise, and surface a small set of products, brands, or solutions that best match the context. Discovery becomes guided rather than exploratory.
This shift dramatically reduces the number of choices the user actively sees. Brands are no longer competing for attention on a crowded results page, they are competing to be included in the AI’s short list of “relevant answers.”
Here’s how this fundamentally changes discovery:
Discovery happens inside the model: The journey doesn’t begin on your website or even on a SERP. It begins within the assistant’s generated response.
Long-tail intent becomes the norm: Users ask highly specific, conversational questions — and AI provides equally specific recommendations.
AI pre-selects products: Instead of browsing, users request refinements (“show me something cheaper,” “something vegan,” “something for sensitive skin”). The user no longer finds products — AI decides which products they see.
This creates a new competitive landscape where early visibility depends not on ranking for keywords, but on becoming the brand an AI assistant trusts enough to surface during discovery.
Consideration – How AI search shapes shopping behaviour
Once AI handles the comparison work, the consideration phase changes fundamentally. In traditional search, users actively gather information: opening multiple tabs, switching between review pages, and filtering options manually. AI collapses that process into a single conversational flow.
Instead of navigating interfaces, users refine their intent through natural questions:
“Is there a cheaper option?”
“Which one is more durable?”
“Show only models suitable for travel.”
Each refinement updates the recommendation set instantly, removing the need for manual comparison. This shift has three major implications:
Friction disappears: The evaluation phase becomes streamlined; no scrolling, no switching between sources, no cognitive overload. Users move from broad interest to a focused shortlist in seconds.
Brand-driven consideration weakens: AI does not prioritize brand familiarity. Instead, it ranks clarity, consistency, and reliability of product data and sentiment. Challenger brands with strong data foundations can outperform established names simply because the model interprets them more accurately.
Decision criteria become explicit: AI systems show why a product is recommended; highlighting factors such as battery life, durability, comfort, or price-to-value. This transparency reshapes how users weigh trade-offs and forces brands to articulate benefits more concretely.
AI replaces the messy, user-driven comparison phase with a guided decision path, driven by signals it considers most relevant.
Conversion – How AI search influences buying decisions and attribution
AI search does not just influence what people choose — it reshapes how and when they decide. By the time a user reaches a product detail page (PDP), most of the evaluation has already happened upstream inside the AI assistant.
1. The funnel compresses
The traditional path: search → compare → review → choose → buy, collapses into a single interaction: ask → receive → purchase.
AI filters irrelevant options, highlights core benefits, and aligns products with the user’s intent before they ever land on a website.
2. Users arrive pre-sold
When someone finally clicks through, AI has already:
removed products that don’t match the intent
surfaced the strongest fit based on specs, sentiment, and context
explained why the product fits
validated the choice with aggregated social proof
At this stage, the PDP functions less as an evaluation step and more as a final confirmation.
3. Zero-click behaviour increases
Because AI assistants provide complete answers, users increasingly skip search results entirely. Clicks happen after the recommendation, not before. For brands, this means visibility at the point of AI-generated selection matters more than ranking on SERPs.
4. Attribution becomes unreliable
Analytics may show a sale as “direct” or “organic,” but the real driver was the AI model that shaped the decision upstream. Understanding attribution now requires recognising that the decision is made before the click — inside the assistant, not on the website.
5. AI decides who wins the sale
When AI pre-selects products, the point of competition shifts. The question is no longer “How do we attract traffic?” but: “How do we become the product AI is confident recommending?”
6. AI enables conversion optimization
In a more indirect way, the use of AI tools helps maximize conversion rates, especially by enabling the creation of high-performing ad visuals and professional-quality product images without the need to hire a professional photographer.
Retention – How AI search extends the relationship after the purchase
AI search doesn’t stop once the user buys a product. Post-purchase, AI assistants continue to guide, support, and influence how customers experience a brand, shaping satisfaction, loyalty, and future purchase behaviour.
Post-purchase recommendations.
Users ask follow-up questions (“Which ear tips fit?”, “What accessories do I need?”), and AI suggests compatible products automatically, turning assistants into continuous upsell engines.
Troubleshooting moves to AI.
Queries like “Why isn’t my device pairing?” are answered using manuals, FAQs, Reddit threads and community insights. Support no longer happens on your website but inside the AI model.
Communities drive post-purchase experience.
Reddit, niche forums and user guides influence onboarding, perceived product quality and future recommendations, all signals AI ingests.
Retention becomes an AI feedback loop.
Positive experiences strengthen the chance of future AI recommendations; negative ones reduce visibility.
Loyalty and churn are increasingly shaped by how AI represents your brand after the sale.
What brands must do to stay visible in AI search
AI search is driven by signals, not shortcuts. To appear in AI-generated recommendations, brands must strengthen the inputs that models rely on: data, context, sentiment and intent alignment. These are not “SEO tactics”, but the foundational elements AI systems use to understand which products are relevant, trustworthy and worth recommending.
Below are the four areas every brand must master to stay visible in an AI-first customer journey.
Strengthen structured product data
AI systems rely on clean, consistent and machine-readable product data.
If a model cannot interpret your product, its attributes, variants, pricing or specifications, it cannot recommend it. Structured data (JSON-LD, detailed attributes, accurate specs) becomes a core visibility signal in AI search.
Build contextual authority across the web
AI learns from the broader ecosystem: expert reviews, comparison sites, creator content, community discussions and contextual backlinks. These signals explain what your product does, who it’s for and how it performs, the context AI needs to justify recommendations.
Maintain consistent review and sentiment signals
Models analyse patterns in reviews, not just ratings. Recurring strengths, recurring complaints, sentiment stability and authenticity help AI understand your product’s real-world performance. Clear, consistent patterns improve recommendation likelihood.
Create content that matches conversational intent
Users ask AI natural, specific questions (“best headphones under 50 for commuting”). Brands must reflect this conversational intent in their content — with natural-language FAQs, long-tail problem descriptions and context-rich product pages. This helps AI map products to real user intent.
AI search is the customer journey now
AI is no longer an add-on to traditional search — it has become the discovery layer that shapes every stage of the customer journey. It determines what users see, how they compare options, which products they trust, and where conversions ultimately happen. Most decisions now form before a user reaches a website, as AI assistants synthesise data, filter noise, and surface only the options that match intent.
For brands, this shifts the central question from:
“How do I rank in Google?” to “Will AI recommend my product when a customer asks for it?”
The brands that win in this new environment are those that invest in structured data, distributed authority, consistent sentiment signals, and content that reflects real conversational intent. These are the signals LLMs rely on to decide which products deserve to surface, and which quietly disappear from the journey.
AI search isn’t just changing how people buy. AI search is where the buying journey now begins, and where the winning brands are chosen.